Table of Contents
Understanding the Silent Threat in Ottawa Homes
Every home in Ottawa, regardless of its age or location, could harbor a hidden danger that silently affects your family’s health. This invisible, odorless threat is radon gas – a naturally occurring radioactive element that seeps into homes from the ground below. As a professional home inspector serving the Ottawa region, I’ve seen firsthand how this silent killer is often overlooked until a proper home inspection reveals its presence. Radon gas is the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking, making awareness and action critically important for Ottawa homeowners.
This comprehensive guide will equip you with essential knowledge about home radon testing, empowering you to identify potential risks and take proactive steps to protect your family. We’ll cover everything from what radon gas is to how professional home inspection services can detect it, interpret test results, and recommend effective mitigation strategies for Ottawa homes.
Key Takeaways
The Dangers of Radon Gas
Video courtesy of Health Canada and the Public Health Agency of Canada
What is Radon Gas?
Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas formed by the breakdown of uranium in soil, rock, and water. As uranium slowly decays, it produces radium, which then breaks down to form radon gas [6]. This invisible gas can migrate through the ground and into the air we breathe. Being completely invisible, odorless, and tasteless, radon gives no warning signs of its presence in your home [2].
Once radon enters your home, it can accumulate, especially in lower levels like basements and crawl spaces, reaching potentially dangerous concentrations. When inhaled, radioactive particles from radon can damage the cells lining your lungs, significantly increasing your risk of lung cancer over time. This makes professional radon testing during home inspections a crucial part of ensuring your Ottawa home is safe.

How is Radon Gas Formed?
Radon gas is formed by the natural radioactive decay process of uranium, which is present in varying amounts in virtually all soil, rock, and water. This radioactive decay follows a specific chain: uranium-238 decays to form radium-226, which then further breaks down to produce radon-222 gas [10]. This process happens continuously in nature, releasing radon into the environment.
What makes radon particularly concerning is its gaseous state, allowing it to move freely through soil and rock, eventually finding its way into homes through various entry points. Unlike other radioactive elements in the decay chain, radon’s gaseous form means it can be inhaled, bringing radioactive particles directly into your lungs where they can cause damage to sensitive tissues. Professional home inspections in Ottawa regularly include radon testing precisely because of this invisible but significant health risk.
Ottawa’s Geological Risk Factors for Radon
The Ottawa region has specific geological characteristics that make homes particularly susceptible to radon gas infiltration. Radon concentrations can differ greatly throughout Ottawa depending mainly on the composition of the local bedrock or soil [75]. Parts of Ottawa are built over uranium-rich bedrock located at relatively shallow depths, creating higher potential for radon gas formation and migration into homes.
The Canadian Shield, which underlies much of the Ottawa region, contains granite formations that typically have higher concentrations of uranium. Additionally, fractures and faults in the bedrock can create pathways for radon gas to travel more easily to the surface [19]. During a professional home inspection in Ottawa, these geological factors are taken into consideration when assessing radon risk potential.
Studies have shown that even homes located on the same street in Ottawa can have significantly different indoor radon concentrations [82], making individual home testing essential rather than relying on neighborhood averages. This variability highlights why professional home inspectors recommend radon testing for all Ottawa homes, regardless of location within the region.
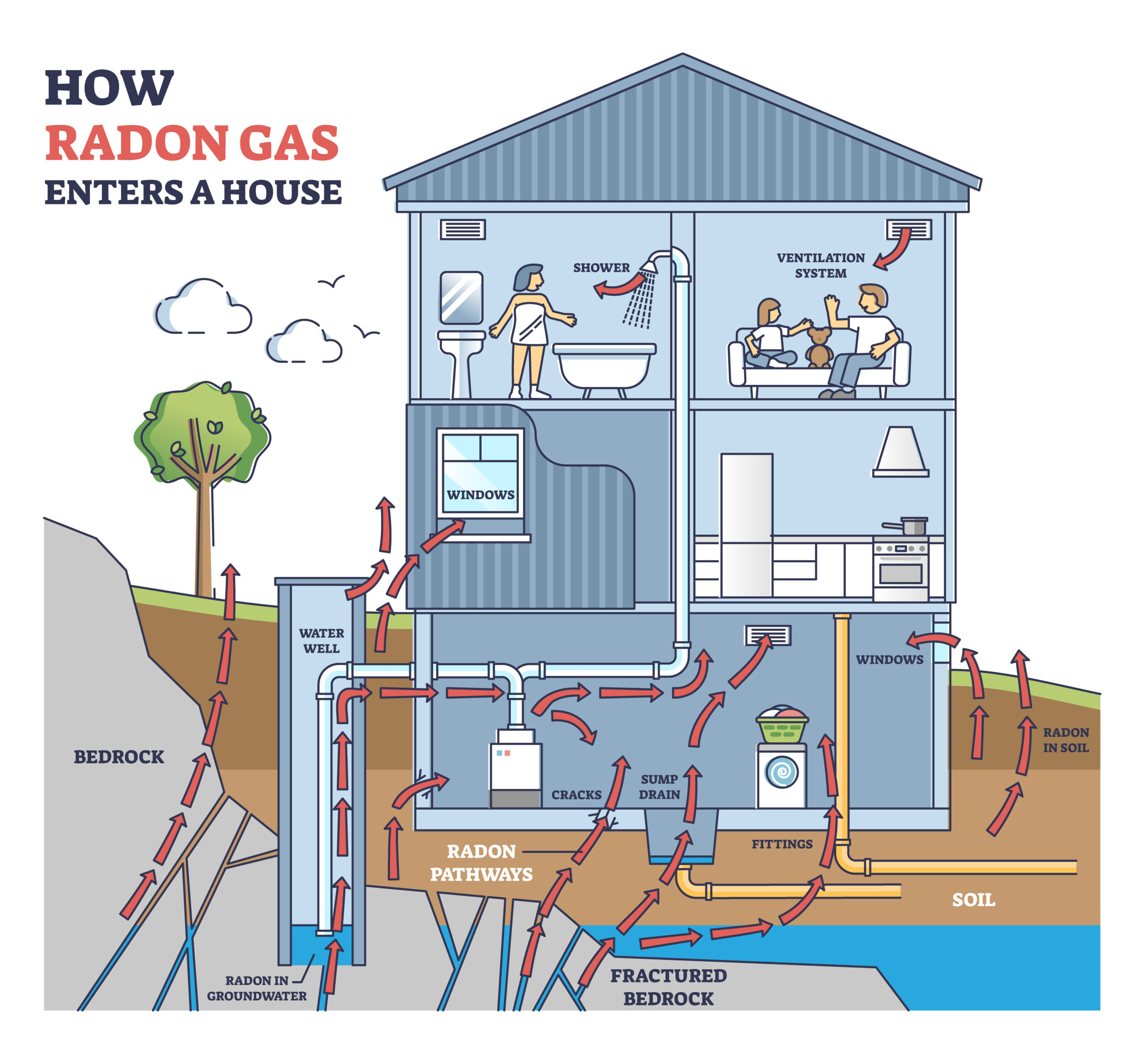
How Radon Gas Penetrates Your Ottawa Home
Well Water
In rural areas around Ottawa where homes use well water, radon can enter through the water supply. Radon dissolves in groundwater that passes through uranium-rich rock formations. When this water is brought into the home and used for showering, washing dishes, or laundry, the dissolved radon is released into the indoor air [29]. Professional home inspections for rural Ottawa properties should always include assessment of potential radon in well water systems.
Cracks in Concrete Basement Floor Slabs
One of the most common entry points for radon in Ottawa homes is through cracks in concrete basement floor slabs. Foundation cracks and joints in concrete slabs provide direct pathways for radon gas to enter from soil into living spaces [30]. Even hairline cracks that may seem insignificant during a visual home inspection can allow significant amounts of radon to enter your home.
Porous Foundation Materials
Radon can also penetrate through seemingly solid concrete, as most concrete is somewhat porous. Even without visible cracks, radon gas can diffuse through foundation materials over time [28]. During a professional home inspection, we look for signs of foundation deterioration that might increase radon penetration.
Exposed Soil in Crawl Spaces
Crawl spaces with exposed soil floors and no vapor barrier present a significant radon entry risk. Homes with crawl spaces can have elevated radon levels due to the vacuum effect drawing radon gas from the crawl space into the home [23]. When performing home inspections in Ottawa, I pay particular attention to crawl spaces that lack proper sealing and ventilation.
Other Entry Points
Radon can enter through various other openings where the house contacts the soil, including:
During a comprehensive home inspection in Ottawa, all these potential entry points are examined to assess radon risk and recommend appropriate mitigation strategies.
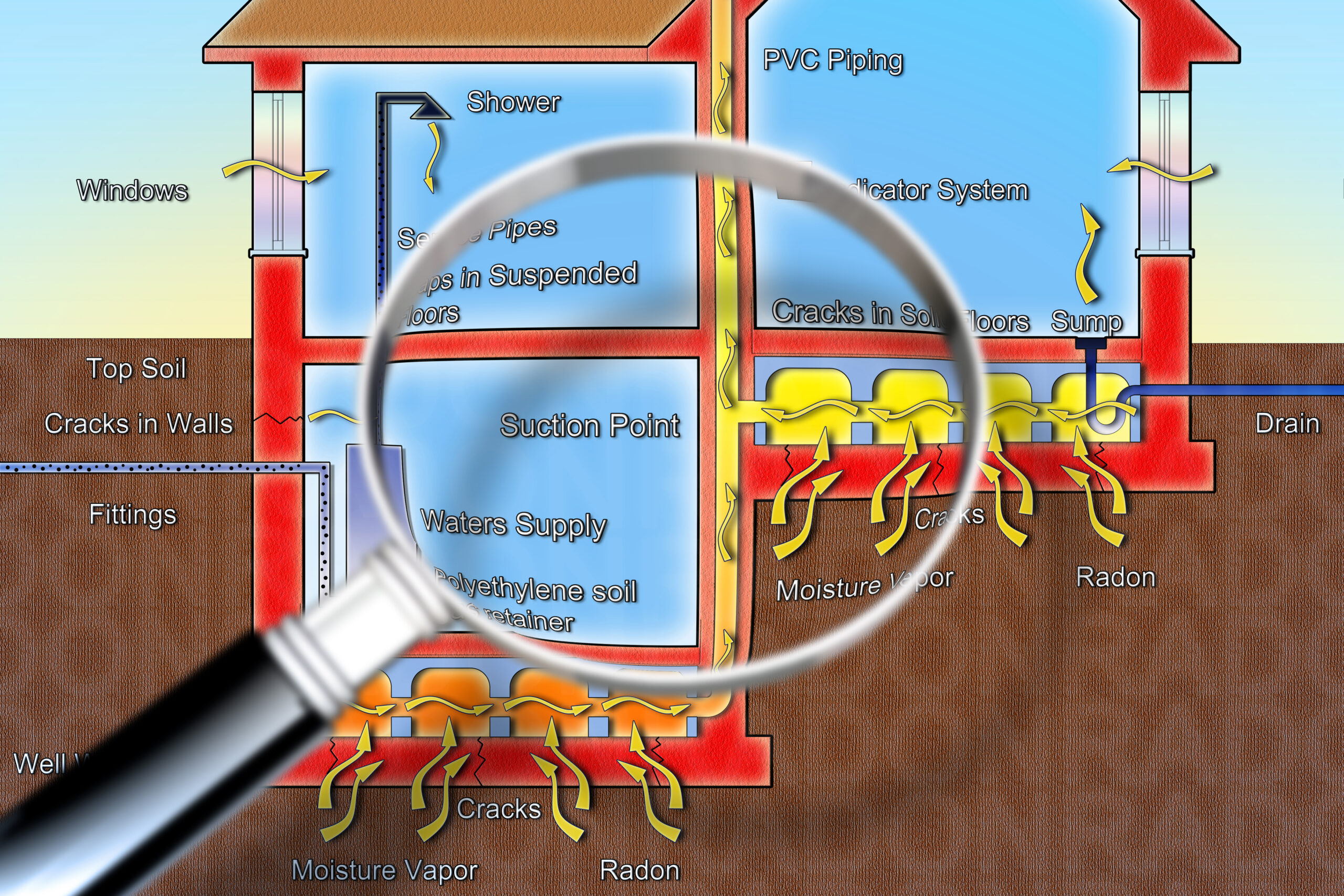
Physical Characteristics of Radon Gas
Radon gas has several physical characteristics that make it particularly dangerous and difficult to detect without proper testing equipment:
These characteristics explain why some professional home inspection services include specialized radon detection equipment – there’s simply no way to detect radon with human senses alone. Without proper testing during a home inspection, radon could be accumulating to dangerous levels in your Ottawa home without any noticeable signs.
What Are Considered Unsafe Levels of Radon Gas?
Canadian Guidelines
Health Canada has established a guideline of 200 becquerels per cubic meter (Bq/m³) for radon in indoor air [33]. This is the actionable threshold at which Health Canada recommends taking steps to reduce radon levels in your home. This guideline was established through collaboration between Federal Provincial Territorial Radiation Protection Committee, taking into account both health risks and the practicality of mitigation.
Warning Levels and Mitigation Requirements
While 200 Bq/m³ is the official action level, Health Canada and radon experts recommend following these guidelines:
Professional home inspection services in Ottawa can help you interpret your radon test results and recommend appropriate next steps based on the specific levels detected in your home.
The ALARA Principle
Health Canada promotes the ALARA principle – keeping radon exposure “As Low As Reasonably Achievable.” While the guideline level for mitigation is 200 Bq/m³, mitigation measures should ideally reduce radon to much lower levels whenever possible [34]. During a home inspection, we can discuss various mitigation strategies to help you achieve the lowest practical radon levels for your Ottawa home.

Radon Monitoring
Radon gas levels between 100 and 200 becquerels per cubic metre warrant continuous monitoring
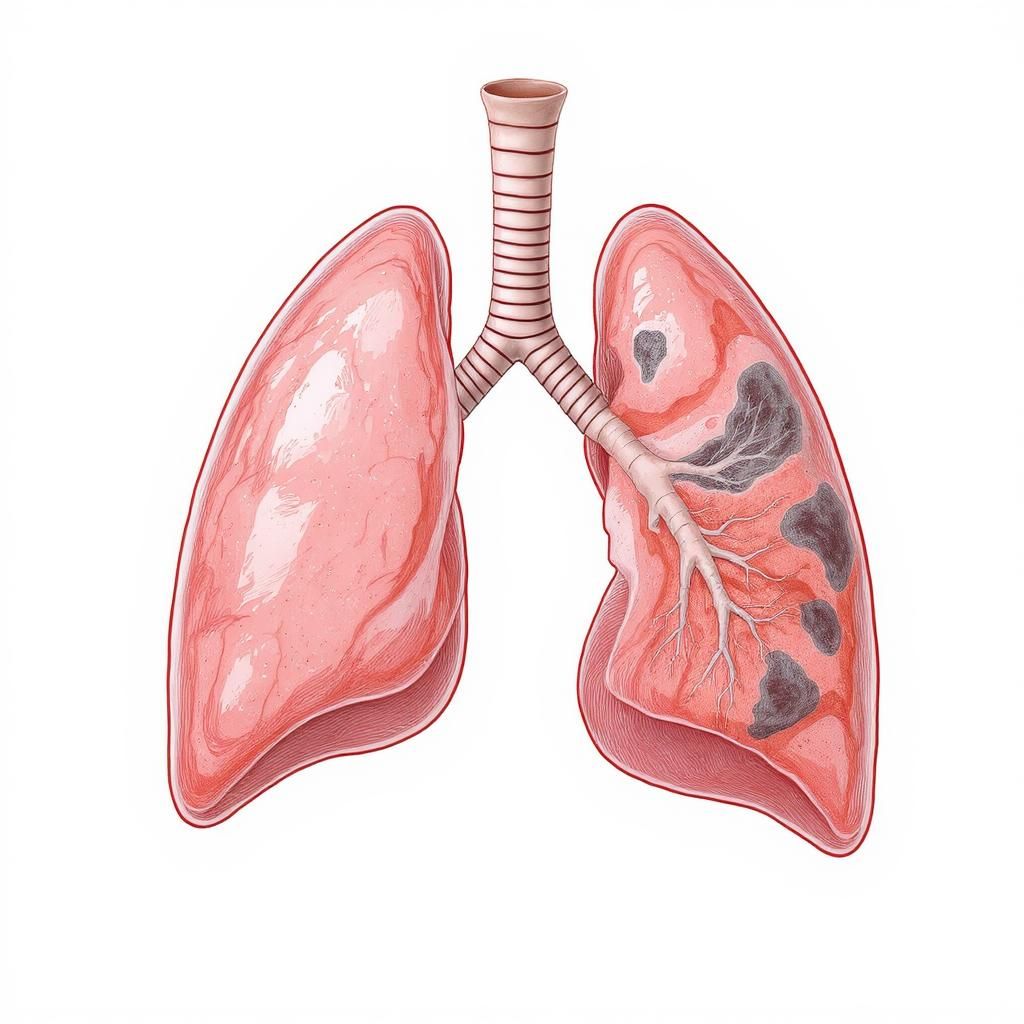
Health Hazards of Radon Exposure
Lung Cancer Risk
The primary health concern with radon exposure is its role in causing lung cancer. When radon decays, it produces radioactive particles that can damage the cells lining the lungs when inhaled. According to Health Canada, radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking, responsible for an estimated 3,200 deaths each year in Canada [2].
The risk increases significantly for smokers exposed to radon, as the effects of smoking and radon exposure together create a synergistic effect. However, even non-smokers are at substantial risk – radon is actually the number one cause of lung cancer in non-smokers [45].
Risks to Pregnant Women and Unborn Children
Research suggests that radon and particle radioactivity may be associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes [43]. While direct studies specifically on radon’s effects on pregnancy are limited, we know that ionizing radiation exposure during pregnancy can pose risks to the developing fetus. As a precautionary measure, pregnant women should be particularly vigilant about radon exposure in their homes.
Genetic Considerations
Chronic exposure to high indoor radon levels has been linked to increased genome oxidative damage [50]. This type of damage can potentially lead to genetic mutations, though more research is needed to fully understand the long-term genetic implications of radon exposure beyond its well-established role in lung cancer development.
During home inspections in Ottawa’s radon “red zones”, I emphasize that radon mitigation is particularly important for households with pregnant women, young children, or individuals with respiratory conditions who may be more vulnerable to radon’s effects.
Professional Radon Testing Options
As a professional home inspector serving Ottawa, I provide comprehensive radon testing services in partnership with LEX Scientific Inc., a leading Canadian environmental laboratory established in 1981 [1]. LEX Scientific has been at the forefront of radon testing in Canada, serving as one of the first independent C-NRPP certified laboratories in the country [2].
Short-Term Radon Testing
Short-term radon tests, often called “snapshots,” use Electret Ion Chambers such as the E-Perm Radon Test Kit by LEX Scientific. These tests are performed over a period of 2 to 10 days and provide quick preliminary results about radon levels in your home [2].
Advantages:
Disadvantages:

Short-term radon tests, often called “snapshots,” use Electret Ion Chambers such as the E-Perm Radon Test Kit by LEX Scientific. These tests are performed over a period of 2 to 10 days and provide quick preliminary results about radon levels in your home.
Long-Term Radon Testing
Long-term tests use RSKS Alpha Track detectors such as the LEXCheck Test Kit by LEX Scientific. These tests measure radon levels over a period of 3 to 6 months, providing a much more accurate picture of your home’s average radon concentration [2].
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
The Canadian National Radon Proficiency Program (C-NRPP) recommends a minimum 3-month test duration for the most accurate results, with 6-month tests providing even greater accuracy. As part of our professional home inspection services in Ottawa, we can help you determine which testing approach is most appropriate for your specific situation.

Radon Mitigation Techniques
If a rapid radon test performed during your Ottawa home inspection reveals elevated radon levels above 200 Bq/m³, various mitigation techniques can effectively reduce radon concentrations to safer levels.
Sub-Slab Depressurization Systems
The most common and effective radon mitigation method is sub-slab depressurization (SSD). This approach involves:
- 1Installing a pipe through the foundation floor slab
- 2Connecting a radon fan (or “pump”) to create negative pressure beneath the home
- 3Venting the captured radon gas safely outside, away from windows and air intakes
The radon fan continuously draws radon from beneath the foundation before it can enter your home, drastically reducing indoor concentrations [53]. During home inspections in Ottawa, I can identify optimal locations for system installation based on your home’s specific construction.
The fan component can be installed in various locations:
In Ottawa’s cold climate, the radon fan is normally installed in the basement, with the vent pipe penetrating through the foundation wall or rim/header joist to the outdoors. Placing the fan inside the heated basement eliminates the possibility of frost buildup within the fan, which could otherwise damage the fan motor. Furthermore, the relatively short exterior pipe segment reduces the amount of condensation and subsequent frost buildup within the vent pipe.
Professional installation ensures the system is properly sized for your home’s specific needs and climatic conditions.

Radon Mitigation
A sub-slab depressurization system, also known as a radon fan, can greatly reduce radon gas levels in the home.
Radon in Well Water Mitigation
For Ottawa homes with well water containing radon, specialized systems are available. The AIRaider 433-S50 by RadonAway is a diffused bubble aeration system specifically designed for removing radon from well water [63]. This system:
Unlike some filtration systems that simply capture radon temporarily, aeration systems permanently remove the radon by releasing it into the outside air [68], providing a more comprehensive solution for homes with radon in well water.
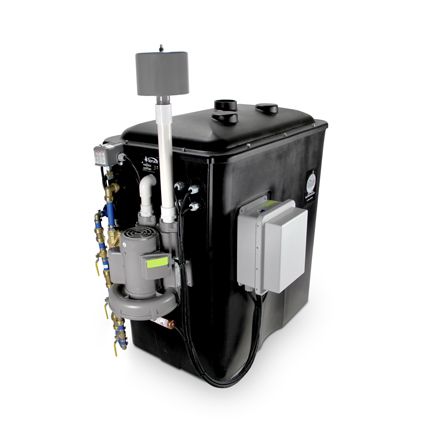

The AIRaider 433-S50 by RadonAway is a diffused bubble aeration system specifically designed for removing radon from well water.
Preventative Measures for Ottawa Homeowners
Even before conducting a professional home inspection or radon test, Ottawa homeowners can take several preventative steps to reduce potential radon entry:
Seal Foundation Cracks and Openings
Sealing cracks in basement floor slabs and foundation walls can help reduce radon entry. Pay particular attention to:
While sealing alone is typically not sufficient to address high radon levels, it complements other mitigation strategies and improves their effectiveness.
Seal Sump Pits
Stormwater sump basins should be sealed with gasketed sump lids designed specifically for radon reduction. These specialized covers allow the sump pump to function normally while preventing radon gas from entering your home through the sump pit.
Address Crawl Spaces
For homes with crawl spaces, consider these radon-reduction steps:
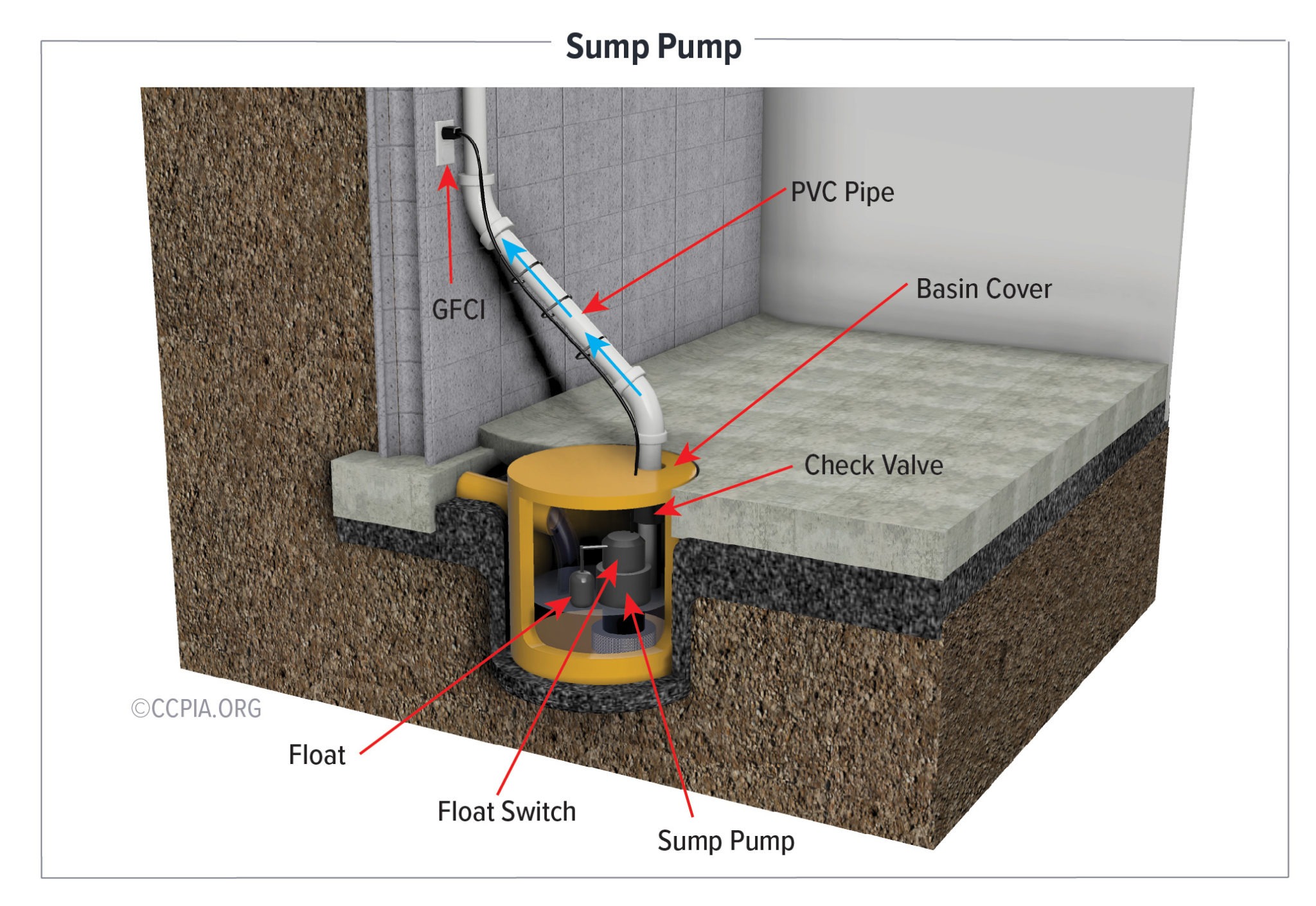
During home inspections in Ottawa, I pay special attention to crawl spaces as they often represent significant radon entry points when improperly sealed or ventilated.
Improve Home Ventilation
While increasing ventilation alone won’t solve serious radon problems, improving air exchange throughout your home can help reduce radon concentrations:
Remember that these preventative measures are supplements to, not replacements for, professional radon testing and mitigation. A thorough home inspection by a qualified professional is the only way to accurately assess your Ottawa home’s radon risk.
Conclusion: Protecting Your Ottawa Family from Radon
As a professional home inspector serving the Ottawa region, I’m well aware of the health hazards attributed to chronic exposure to high levels of radon gas. The unique geological characteristics of the Ottawa area make radon testing an essential part of responsible homeownership in our region.
The good news is that through professional home inspection services, including comprehensive radon testing, you can identify and address this invisible threat. Whether you’re purchasing a new home, renovating your current residence, or simply want peace of mind about your family’s health, radon testing should be part of your home safety plan.
Our partnership with LEX Scientific Inc. allows us to offer both short-term and long-term radon testing options to meet your specific needs. If elevated levels are discovered, professional mitigation can reduce radon concentrations by up to 99%, effectively eliminating this health risk from your home.
Don’t let the “silent threat” of radon compromise your family’s health. Contact our professional home inspection team today to schedule radon testing for your Ottawa home. Your proactive decision could quite literally save lives.
Are you concerned about radon in your Ottawa home? Our professional home inspection services include comprehensive radon testing to protect your family’s health. Contact us today to schedule your radon test or to learn more about all of our home inspection services.
References
- Lex Scientific inc.
- Radon
- Radon
- Radon – What you need to know
- What is radon?
- CCOHS: Radon in Buildings
- Radon in Your Home
- Frequently Asked Questions about Radon
- Radon: What you need to know
- Residential radon
- Radon | Inspection, Compliance and Enforcement
- Radon Guide
- Ottawa-Gatineau-Radon
- Radon in Your Home
- Radon gas: it’s in your home
- Geoscience Canada Volume 19 Number 4
- Guide for Radon Measurements in Residential Dwellings
- Preliminary Radon Assessment for a Used Fuel Deep …
- Distance to faults as a proxy for radon gas concentration in …
- Radon Potential of the National Capital Region
- Uranium, radon, helium and other trace elements and …
- Radon in Canada’s Uranium Industry
- How Can Radon Enter a Home
- Radon – Reduction Guide for Canadians
- Does radon go through concrete or only cracks?
- How Radon Gas Sneaks into Homes
- How Does Radon Enter Your Home?
- How Radon Enters A Home
- Radon Risk
- How Radon Seeps Through Foundation Gaps: Entry Points
- How Radon Enters Your Home
- Residential radon
- Radon guideline
- Guide for radon measurements in homes
- Radon
- Radon mitigation options for existing buildings
- Radon: radon thresholds by country/ region
- Cross-Canada Radon Survey
- Radon in the workplace
- Radon
- Radon levels: What do they mean?
- Reducing Radon Levels in Existing Homes
- Exposure to radon and ambient particle radioactivity during …
- RESIDENTIAL RADON AND BIRTH DEFECTS
- Radon—The Element of Risk. The Impact …
- Radon gas: it’s in your home
- Ionizing radiation and health effects
- Health Risk of Radon | US EPA
- The health effects of radon and uranium on the population of …
- Oxidative genomic damage in humans exposed to high …
- Radiation and Health Effects
- Health/Environment Issues Linked to the Nuclear Fuel Chain
- Radon – Reduction Guide for Canadians
- Understanding Radon Mitigation: Sub-Slab Depressurization
- How To Install a Radon Mitigation System
- DIY Radon Mitigation: A Step-by-Step Guide to …
- Sub-slab Depressurization (SSD) Tech Sheet – vim – ITRC
- Consumer’s Guide to Radon Reduction – How to Fix Your …
- Radon Mitigation
- Radon System Design & Pressure Field Diagnostics (PFD)
- The Anatomy of a Radon Mitigation System
- The Ultimate Guide for Radon Mitigation (SSD) System
- AIRaider™ 433-S50 – 115V Radon in Water Removal System
- AiRaider 433-S Series Diffused Bubble Radon Aeration, …
- AIRaider™
- Radon Aeration Systems.. for Well Water
- Installation & Operation Manual
- AIRaider: The Most Effective Way to Remove Radon from Water
- AiRaider 433-S50X 1 inch (28473) 115V Radon / VOC …
- Aeration Systems
- AIRaider Aeration Radon Removal System
- 2019/20 PRODUCT CATALOG RADONAWAY.COM
- Cross-Canada Radon Survey
- Cross-Canada Survey of Radon Concentrations in Homes
- Ottawa-Gatineau-Radon
- Risk of Residential Radon Exposure Varies Geographically
- Radon in Canada’s Uranium Industry
- Geoscience Canada Volume 19 Number 4
- Radon Potential of the National Capital Region
- Comprehensive survey of household radon gas levels and …
- Preliminary Radon Assessment for a Used Fuel Deep …
- A Summary of Residential Radon Surveys and the …







